The most commonly used ratios in finance.
How to interpret the text:
Data types presented in RED are downloadable data
If ratios or their components are not ready for download I try to present ways to calculate them (indirectly)
1. Debt to equity ratio
2. Current ratio
3. Quick ratio
4. Return on equity (ROE)
5. Net profit margin
1. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Total Liabilities / Shareholders Equity
Shareholder equity = book value x number of shares
Compustat
Direct download: DLC
DLC represents the total amount of short-term notes and the current portion of long-term debt (debt due in one year).
LT = Total liabilites
BKVLPS (book value per share)
(CSHO) Common Shares Outstanding
Formula:
LT / (BKVLPS x CSHO) = debt to equity
Amadeus
Book value per equity = Book value per share x number of shares outstanding
Instead of Book value of equity, Market Value ( MV) can be used (market capitalisation)
(closing price x shares outstanding)
In Amadeus only closing price frequencies monthly and weekly, not daily
And: market value per year can be downloaded
Total liabilities = current liabilities + long term liabilities
Formula:
Total debt / total (shareholder) equity = Total liabilities / (market capitalisation x number of shares outstanding) OR (market capitalisation x book value per share)
Datastream*
WC03351 Total liabilities:
WC03995 Shareholder equity: (book value per equity)
NOSH Number of shares outstanding
Instead of Book value of equity, Market Value ( MV) is used (market capitalization)
Market Value MV = share price (P) x number of shares (NOSH) (market capitalisation)
Formula:
1. WC03351 / WC03995
2. WC03351 / MV
*) using search terms debt equity ratio in datatypes provides to following data producing datatypes:
WC08231 (total debt % common equity); WC08221 (total debt % total capital/std); WC08231A (total debt % common equity); WC08231R (total debt % common equity) !! Not all companies provide data. Error types like No data values found; no world scope data; access denied
For more downloadables on income statement and balance sheet see this
2. Current Ratio (working capital ratio)
Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Compustat
Current assets total / current liabilities = current ratio
ACT = Current assets total
LCT = Current Liabilities - Total
Formula:
Current ratio = ACT / LCT
Amadeus
Formula:
Current ratio Current assets total / current liabilities
Datastream
Formula:
WC08106 Current ratio = (current assets total [WC02201] / current liabilities [WC03101] )
Only industrials apply
3. Quick Ratio (quick assets ratio)
(Current Assets – Inventories) / Current Liabilities
Compustat
INVT -- Inventories - Total
ACT = Current assets total
LCT = Current Liabilities - Total
Formula:
(ACT - INV) / LCT
Amadeus
Inventories not in AMADEUS
Datastream
Quick ratio WC08101
Inventories total WC02101
Current assets WC02201
Current liabilities WC03101
Formula:
(WC02201 - WC02101) / WC03101 = WC08101
Not all companies provide data
4. Return on Equity (ROE) (return on net worth)
Net Income / Shareholder's Equity or
(net earnings (after taxes) - preferred dividends) / common equity
Compustat
NI Net income
(BKVLPS x CSHO) shareholder equity
BKVLPS (book value per share)
CSHO Common Shares Outstanding
Formula:
NI / (BKVLPS x CSHO)
Amadeus
P/ L for period = Net Income
Book value per share x number of shares outstanding = Book value per equity
ROE using net Income %
Formula:
(P/L) / (Book value per share x number of shares outstanding) = ROE
Datastream
ROE (total): WC08301
WC03995 Shareholder equity: (book value per equity)
NOSH Number of shares outstanding
Instead of Book value of equity, Market Value ( MV) is used (market capitalization)
Market Value MV = share price (P) x number of shares (NOSH) (market capitalisation)
Formula: WC01001 / MV = WC08301 OR WC01001 / WC03995 = WC08301
5. Net Profit Margin
Net Profit / Net Sales
Compustat
Gross profit margin
Gross Income / Net Sales or Revenues * 100 = UGI / SALE x 100
Gross profit: GP (loss)
Gross income: UGI
. the difference between sales or revenues and cost of goods sold and depreciation.
Net sales or revenues: SALE (sales/turnover)
gross sales and other operating revenue less discounts, returns and allowances.
REVT = Revenue - total
GP = UGI / SALE x 100
Addition Compustat from (copyright) WWU Münster Data- items and ratios
Amadeus
Gross profit
Profit margin (%)
Sales
Formula:
Gross profit / sales (not exactly)
Datastream
DWNM = net profit margin
WC01001 Net sales or revenues
WC01540 Net profit( operating income)
* Components can't be all downloaded. Not all companies provide data
LINKS
Compustat: For more downloadables on income statement and balance sheet see this
Amadeus: For more downloadables on income statement and balance sheet see this
Datastream: for more downloadables on income statement and bsalance sheet, see this
Basic information on financial databases: cook books, tips and tricks & economic news
This blog contains schematic easy to grasp - hands on - help in performing searches in economic databases, making work sets and making them inter-exchangeable between the databases.
* Disclaimer. I am not a finance professional. Most posts are the result of personal findings.
Note:
All presented images are scaled and can be enlarged to original size (click the picture).
* Disclaimer. I am not a finance professional. Most posts are the result of personal findings.
Note:
All presented images are scaled and can be enlarged to original size (click the picture).
Search This Blog
Showing posts with label Ratio's. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Ratio's. Show all posts
8/16/2016
12/12/2014
Datastream: expressions, charting and both
(changed, Dec. 12, 2014)
Datastream offers a wide range of
ready made expressions and functions, which can save considerable time compared
to doing your own calculations. Think of (standard)Deviation, Moving average,
Cumulative sum etc.
Charting
Menu
This a a "dirty, but
easy" method of finding expressions and functions in Datastream.
Open naviator
In Criteria selection press link
Charting
The charting screen opens
It can happen that the results of
another user are presented.
Clear the data with the white
leaflet.
If you want to search for items and
data, the arrow buttons open new menus.
(examples)

The principles are similar to the
regular search screens.
Comparing a fund with an index
might produce a useless chart (equities and indexes are different entities,
after all)
Absolute values
Note the Ahold line (blue)
Shown are the default
datatypes (price)
There are ways to make this comparison more useful.
Return Index Ri
These are still absolute values... better is to go for relative values/ changes..
changes like moving average.
MAV#(AMSTEOE(RI),1Y) and
MAV#(H:AH(RI),1Y) or PCH (percentage change)
Button ƒx calls up a menu
Mouse over:
Note the bottom three options.
USE stored expressions...
After pressing the option the following
(large) menu appears:
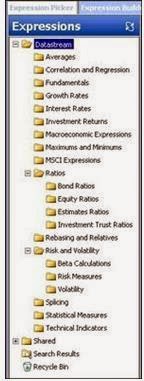
Note ratios and regression, risk and volatility
Sticking to Return Index and Moving
Average, filterings result in
(note search term in top bar)
Moving average
Historical Beta
As you can see
searching for expressions like betas and such with this menu is not
complicated.
All presented
expressions and formulas can be copied and used in another Datastream menu.
When you're not
interested in a chart but in figures, another option is to use the
Datastream Menu (Expression picker/ builder)
From the Datastream
menu press:
The result looks familiar. But pay
attention to the 2nd TAB.
When this is too hard core, there is the same ƒx button available on the menu screen:
Moving average:
Looking
up Expressions in the Extranet:
Popular
functions and expressions < click to open
Mentioned are:
Percentage change
Historical Beta
Moving average
Annualised volatility
etc.
Also look up info in these posts:
A couple
of terms
1)
Volatility
Volatility refers to the amount of
uncertainty or risk about the size of changes in a security's value. High
volatility means that the price of the security can change dramatically
over a short time period in either direction.
Measuring:
A statistical measure of the
dispersion of returns for a given security or market index. Volatility can
either be measured by using the standard deviation or variance between returns
from that same security or market index. Commonly, the higher the volatility,
the riskier the security.
Historical
Volatility
The realized volatility of a
financial instrument over a given time period. Generally, this measure is
calculated by determining the average deviation from the average price of a
financial instrument in the given time period. Standard deviation is the most
common but not the only way to calculate historical volatility.
Implied
volatility
In addition to known factors such
as market price, interest rate, expiration date, and strike price, implied
volatility is used in calculating an option's premium. IV can be derived from a
model such as the Black-Scholes Model.
The estimated volatility of a
security's price. In general, implied volatility increases when the market is bearish and decreases when the market is bullish. This is due to the common belief that
bearish markets are more risky than bullish markets.
Bearish
Believing that a particular
security, a sector, or the overall market is about to fall.
Bullish
Believing that a particular
security, a sector, or the overall market is about to rise.
(Sources Investopedia and
Investorwords.com)
Labels:
charting,
Datastream,
expression builder,
expressions,
moving average,
PCH,
Ratio's,
return
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)